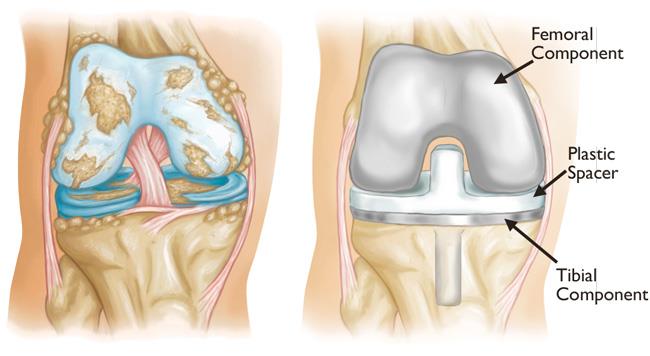
A total knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a safe and effective surgical procedure that treats pain and disability in the knee. It is typically required when nonsurgical treatments such as medication or walking aids are no longer effective, and the patient finds it painful or difficult to do simple activities like walking or climbing stairs.
The procedure involves replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial joint (prosthesis) made of metal alloys, high-grade plastics and polymers.
patients whose knee joints have been damaged by either progressive arthritis, trauma, or other rare destructive diseases of the joint can consider a total knee replacement surgery. Your orthopaedic surgeon will assess your knee’s range of motion, stability and strength. A knee replacement helps to relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help the patient resume normal activities.
As with any surgical procedure, complications can occur. Some possible complications may include, but are not limited to, the following:
The complication rate following a total knee replacement is low. Serious complications, such as a knee joint infection, occur in fewer than 2% of patients. However uncommon these complications may be, they can prolong or limit full recovery should they occur.
You should discuss any concerns thoroughly with your orthopaedic surgeon prior to surgery.